Secure with SSL
Securing the DBmarlin Server UI and API with SSL Certificates
By default the DBmarlin UI and API are accessed via HTTP on port 9090 which goes via an Nginx server process which runs as part of the DBmarlin installation. In order to use HTTPS with an SSL Certificate you have 2 options.
- Use a load balancer or other reverse proxy - which is placed in front of the DBmarlin server to terminate the SSL and pass requests on to it.
- Run SSL on the DBmarlin server itself - which can be done by configuring the DBmarlin Nginx server.
There are pros and cons to these options. Usually having a load balancer terminate the SSL connection is preferable since it offloads any encryption/decryption from the DBmarlin server itself to another device. Also it is often possible for a load balancer to auto-renew the certificate as it approaches its expiry date meaning you aren't left with a broken system if the certificate renewal was forgotten. Amazon ELB and other cloud vendors will usually automatically renew certificate for you for example. The downside is that the addition of a load balancer may come at an extra cost which is why we support using the DBmarlin Nginx server for SSL handling.
Using a load balancer or other reverse proxy
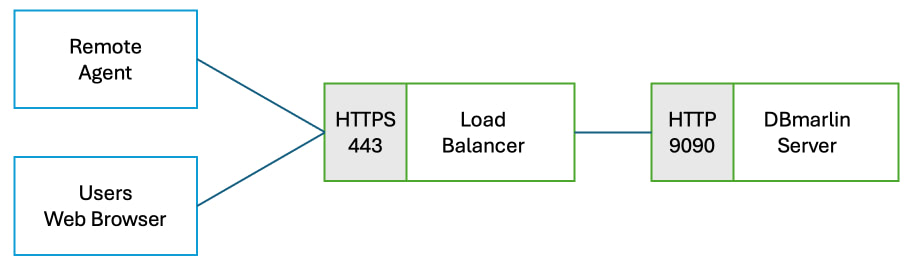
If you are using an external load balancer then setup a listener for protocol=HTTPS and port=443 and assign the SSL certificate you want to use which matches the DNS name by which you are going to access the DBmarlin UI and API. In the load balancer rules set the target as the the DBmarlin server's host or IP using protocol=HTTP and port=9090.
Run SSL on the DBmarlin server itself
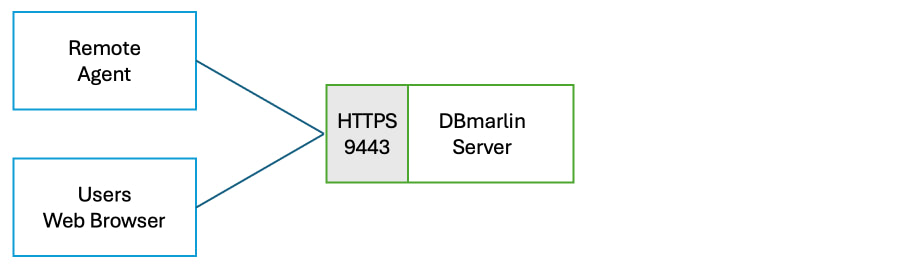
If you want to setup SSL on the DBmarlin server instead you can configure Nginx by renaming the ssl.conf.example file to ssl.conf
cd dbmarlin/nginx/conf
mv ssl.conf.example ssl.conf
The ssl.conf is as shown below but can be customised as required. The example is looking for a certificate file called cert.pem and private key called key.pem in the same conf directory as the ssl.conf file. If your certificate and private key have different names or locations then then ssl.conf should be modified to use the correct names.
server {
listen 9443 ssl;
server_name localhost;
ssl_certificate cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key key.pem;
include shared_server.conf;
}
Generating a certificate
For testing you can generate a self-signed cert and private key as shown below. This command will generate key.pem and cert.pem in the dbmarlin/nginx/conf directory.
For production you should generate a proper certificate using a Certificate Authority.
cd dbmarlin/nginx/conf
openssl req -x509 -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 \
-keyout key.pem \
-out cert.pem \
-days 365 \
-subj "/CN=localhost"
Restart Nginx
Restart Nginx to pick up the new config and see that is it listening on port 9443.
./stop.sh -n && ./start.sh -n
netstat -nalp | grep LISTEN
Configuring Remote agents work with SSL certificate
The remote agent needs to communicate with the Archiver API to send monitoring data which the Archiver writes to the DBmarlin repository. This can also use an SSL encrypted connection. In order for the remote agent to trust the certificate it needs to be in the Java KeyStore (JKS) which lives in dbmarlin/java/[jdkversion]/lib/security/cacerts
List certificates already in the Java KeyStore
This will show a long list of root certificates that are bundled with Java by default which include the main Certificate Authorities on the internet.
cd dbmarlin/java/[jdkversion]
./bin/keytool -list -v -keystore ./lib/security/cacerts -storepass changeit
Add a new certificate to the Java KeyStore
Rather than adding the individual certificate to the Java KeyStore which might only have a relatively short expiry date, you should add the root certificate which will normally have a much longer expiry date. Assuming the root
cd dbmarlin/java/[jdkversion]
./bin/keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias my-root-ca -file my-root-ca.crt \
-keystore ./lib/security/cacerts -storepass changeit
Restart the remote agent after adding a new certificate.